Você sabia que o NPS tem uma atualização? O NPS 3.0 é a nova versão da metodologia Net Promoter Score, famosa por medir o nível de satisfação e lealdade dos clientes com os produtos, serviços e marcas.
Amplamente utilizada pelos times de atendimento e sucesso ao cliente, a métrica passa a abranger também ganhos financeiros, tornando mais palpáveis lucros e respostas financeiras por trás da lealdade e satisfação do consumidor.
Para te atualizar sobre essa mudança, vamos falar mais sobre o NPS 3.0, como calcular e implementar no seu negócio. Acompanhe!
O que é NPS 3.0? Entenda a evolução da métrica
O NPS (Net Promoter Score) foi introduzido por Fred Reichheld, em 2003, em seu artigo publicado na Harvard Business Review.
A métrica, que olha para a satisfação do cliente, consiste em fazer uma única pergunta simples e rápida aos clientes: “Em uma escala de 0 a 10, o quanto você recomendaria nossa empresa/produto/serviço a um amigo ou colega?”
Com base na resposta, os clientes são categorizados em três grupos:
- Promotores (notas 9-10): aqueles que promovem sua empresa, falam bem do produto e dão indicações espontâneas.
- Neutros (notas 7-8): não tem nada a se queixar, mas dificilmente fará o esforço de te indicar para alguém, seja negativamente ou positivamente.
- Detratores (notas 0-6): já tiveram experiências negativas e tendem a falar mal da empresa para terceiros. Podem ser prejudiciais para a reputação do negócio.
A partir das notas, o cálculo é feito subtraindo a porcentagem de detratores da porcentagem de promotores para entender qual o nível de satisfação do cliente com um negócio.
A partir dessa simples métrica surgiram algumas evoluções para introduzir insights mais profundos à nota. Com isso, além de apenas buscar o quantitativo, muitas empresas passaram a introduzir questões abertas para buscarem feedbacks qualitativos para que de fato se entenda um pouco melhor o porquê da nota dada.
Até que chega o NPS 3.0, que mantém seu princípio de entender satisfação e lealdade do cliente, mas passa a olhar também para como isso dá resultados reais e financeiros para o negócio. Ou seja, ele tem o objetivo de medir também o crescimento da empresa com base na satisfação do cliente.
Essa atualização tem muita importância pois passa a levar em conta a experiência do cliente, que é o grande foco da relação entre empresa e consumidores nos dias atuais.
Para isso, é adicionada à métrica o EGR, Earned Growth Rate, ou taxa de crescimento ganho. Com a nova métrica, é possível enxergar mais rapidamente os lucros – ou não – por trás dos clientes que são leais, reunindo dados para se pensar em custos e projetar se eles se tornarão lucrativos a longo prazo.
Qual a diferença do NPS 3.0 para as versões anteriores?
Como diversas metodologias, o NPS se aprimorou devido às necessidades de mercado e evolução dos negócios. De forma resumida, as grandes diferenças de suas versões a partir dos livros do autor, são:
- NPS 1.0 – The Ultimate Question: o início da metodologia busca explicar e introduzir o sistema NPS e suas estatísticas: como entender, melhorar e aplicar ao negócio.
- NPS 2.0 – The Ultimate Question 2.0: foca no gerenciamento de sistema de NPS, introduzindo mais análises quantitativas e já focando em resultados financeiros e diferenciais competitivos
- NPS 3.0 – Winning on Purpose: apresenta as melhores práticas do NPS, potencializando o uso da metodologia nas empresas e, definitivamente, focando na relação de experiência e receita.
Earned Growth Rate (EGR): A relação entre satisfação do cliente e crescimento de receita
Como dissemos, O NPS 3.0 baseia-se no Earned Growth Rate (EGR), que mede o crescimento da receita gerado por clientes recorrentes e suas referências, além de permitir entender melhor de onde está vindo o lucro em relação a satisfação.
Sendo assim, antes de entender como se calcula o NPS 3.0, é preciso entender sobre o EGR. Para o cálculo do Earned Growth Rate é preciso entender seus dois componentes, que são:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention ou Retenção de Receita Líquida): essa mede a receita gerada a partir de clientes ativos que já compraram da empresa em um período específico.
- ENC (Earned New Customers ou Novos Clientes Conquistados): mede o valor do crescimento de receita vindo de novos clientes através de indicação.
Cálculo NPS 3.0: Entenda como medir a evolução do Net Promoter
Agora que você sabe o que é o EGR, vamos ao cálculo do NPS 3.0: Para calcular o EGR, é preciso somar o NRR e o ENC e depois, subtrair 100 do resultado. Ao fazer isso, temos a taxa de crescimento ganho.
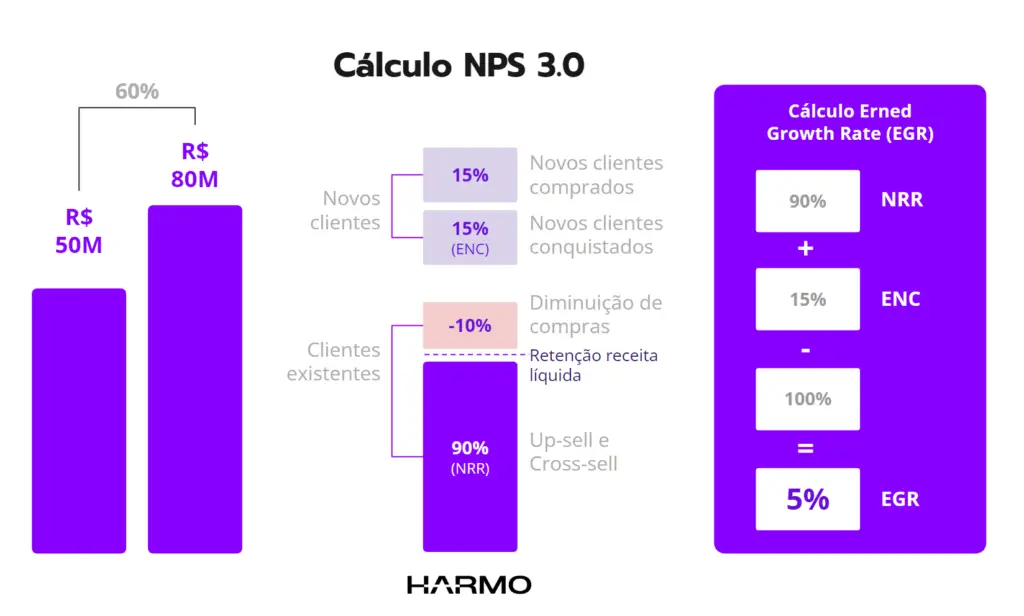
Vamos pensar de forma prática: a receita de uma empresa passou de R$50M em 2023 para R$80M em 2024. Desse crescimento, 90% vêm de clientes existentes (NRR), enquanto 15% vieram de novos clientes (ENC). Sendo assim:
EGR = 90 (NRR) + 15 (ENC) – 100 = 5%
Com isso, a taxa de crescimento ganho foi de 5% para o negócio.
Passos práticos para implementação do NPS 3.0
O NPS 3.0 vai além da busca de respostas do cliente e é preciso ter dados e bases dentro de casa para que os cálculos sejam corretos. Portanto, é essencial investir em como seu negócio tem coletado dados ao longo do tempo e, mais do que isso, em como de fato são contabilizadas as entradas de seus clientes.
1. Invista em dados
Para que o cálculo tenha resultados verdadeiros, é preciso saber de fato quanto rende seus clientes e, mais do que isso, quanto passam a render os clientes que chegam por indicação.
Aqui pode ser o grande desafio, afinal, muitas empresas não conseguem medir a entrada daqueles que indicam. Portanto, para ter efetividade em seu NPS 3.0, é preciso investir em formas de segmentar e criar base de dados.
Saber como seu cliente chegou ao seu negócio é essencial não apenas para essa métrica, mas também para saber o que dá certo ou não, para investir em canais e para criar estratégias de ponta a ponta para o negócio.
2. Entenda as métricas utilizadas para seu negócio
Muitas são as métricas de atendimento, sucesso do cliente e experiência e é preciso ter em mente que nem todas vão fazer sentido para seu negócio. Não basta pegar todas as métricas existentes e calcular apenas para ter em uma planilha, afinal, elas devem ser guias para entender o que está sendo sucesso ou não e para trilhar caminhos para inovação e melhorias no negócio.
Não basta implementar diversos números que ficam perdidos e não fazem diferença de fato no resultado do negócio. Portanto, antes de utilizar o NPS 3.0, olhe para dentro de casa: o NPS já foi implementado? Os resultados dos promotores e detratores já eram vistos no seu negócio?
Não adianta buscar inovar com a atualização se o NPS “original” não é bem implementado no negócio, faz sentido?
3. Experiência em primeiro lugar
A lealdade dos clientes vai vir a partir das boas experiências que têm com o negócio, portanto, é preciso investir em experiência, personalização e atenção a cada ponto da sua jornada para, aí sim, implementar o NPS 3.0.
Somente com boas estratégias de experiência é que passa a fazer sentido olhar para seus clientes e indicações de forma financeira a partir de uma métrica.
Conclusão
Quanto a experiência já é importante para seu negócio e o quanto a lealdade e satisfação dos clientes já eram medidas? É importante se manter atualizado das métricas e inovações de mercado, mas é também necessário entender o que faz sentido para sua realidade para que as métricas realmente guiem para mudanças e para ações práticas para o sucesso do negócio.
O NPS 3.0 já pode passar a fazer sentido em seu negócio? Aproveite que agora sabe mais sobre ele, reflita se sua empresa mapeia clientes vindos de indicações e invista cada vez mais em experiência e no seu cliente como centro!


